In an increasingly discerning market that values quality and environmental integrity, the certification of carbon credits according to internationally recognized standards is a fundamental aspect to ensure transparency and reliability.
Currently, several standards exist; however, one of the most authoritative and reputable globally is the Gold Standard for the Global Goals, a central reference for those aiming to develop decarbonization projects with verifiable and traceable impact.
How does the Gold Standard certification of carbon credits works?
Everything begins with a solid idea: developing a project that reduces greenhouse gas emissions and generates social and environmental benefits, such as our improved cookstove and water access initiatives.
Each carbon credit project must:
- Demonstrate additionality: prove that emissions would have remained high without the intervention.
- Apply an approved methodology depending on the project type.
- Contribute positively to the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
SDG 13 is mandatory, while at least two additional SDGs must be selected, considering the project type and co-benefits.
To demonstrate all of this, baseline analyses are conducted to assess the ex-ante impact. For example, in projects related to improved cookstoves, kitchen performance test, baseline technology usage survey, end-user survey and baseline stove efficiency test (i.e., water boiling test) are utilized.
These data are included in the Project Design Document (PDD), which represents the second step and serves as a foundation for ex-post analysis and monitoring.
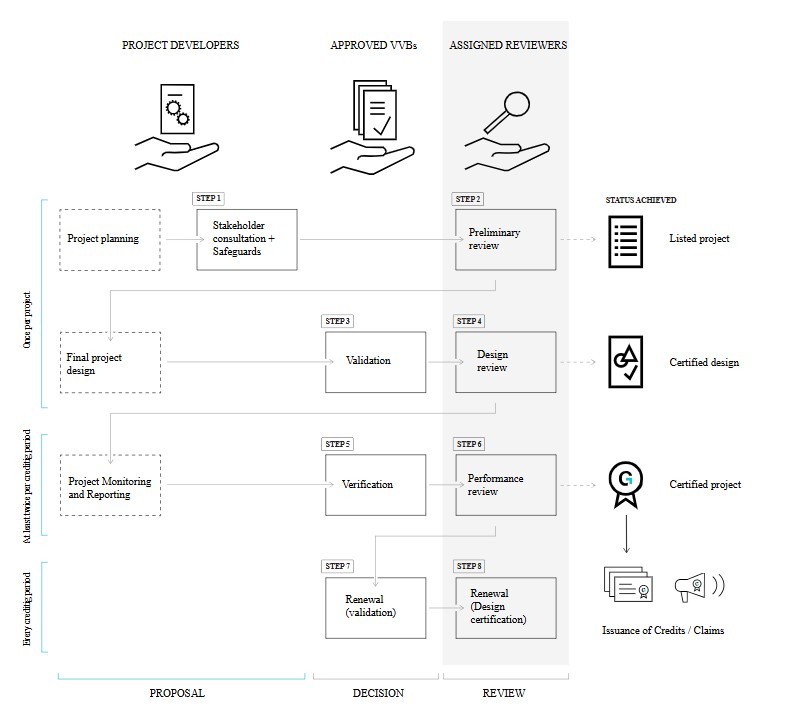
Once the project is defined, the actual design phase begins. The Project Design Document (PDD) needs to be prepared, this is the first official document of the project and must specify:
- how emissions are reduced
- which official methodologies are used
- how results will be monitored
- what risks exist and how they will be managed
Simultaneously, the stakeholder consultation process is initiated to involve local communities and other stakeholders. Gold Standard places great importance on transparency; therefore, organizing this stakeholder consultation is mandatory. The goal is to ensure that the project is well understood, that benefits are clear, and that any concerns are collected and, if possible, addressed.
The PDD includes the following sections:
- detailed project description
- additionality analysis
- calculation of avoided emissions
- monitoring plan
- strategy for SDG co-benefits
Once the PDD is ready, it will serve as the basis for evaluating the entire project. The PDD can undergo a preliminary review before the final version is submitted for validation by a third-party entity.
The PDD is submitted for validation by an accredited independent Validation and Verification Body (VVB).
The VVB reviews all documentation and verifies that the project is technically sound, genuinely additional, and compliant with the chosen methodologies. Transparency of stakeholder consultation and approval of the monitoring plan are also considered.
If the VVB approves, registration can proceed.
With a positive validation report, the project is submitted to Gold Standard.
After a final review, if everything is in order, the project is officially registered and entered into the global database.
This step makes the project official and eligible to generate certified carbon credits, but it does not yet imply the issuance of credits: monitoring data are required first.
Once the project is operational, the project developer must systematically collect data to demonstrate the amount of emissions reduced or removed and the tangible benefits for local communities.
Monitoring surveys are usually used to collect ex-post data. Subsequently, the project developer must prepare an annual monitoring report and submit it for a new external verification.
The monitoring report undergoes a new external verification by an independent VVB.
If verification confirms the results, a Request for Issuance is sent to Gold Standard. External auditors and the Secretariat evaluate the documents and may grant or deny the issuance of credits.
If everything is compliant, Gold Standard issues the certified carbon credits: each credit represents one ton of CO₂ avoided or removed from the atmosphere.
These credits are registered in the Gold Standard Impact Registry and can be sold to companies or individuals wishing to offset their emissions, or used for corporate social responsibility (CSR) projects to achieve carbon neutrality goals.
Link to the OffgridSun registry →
Validation and verification must be periodically renewed for a project to remain registered with Gold Standard. Although the interval may vary depending on the project type, this usually occurs every 5 years.
Interested in learning more?
"*" indicates required fields